What is a Washer?
What is a Washer?
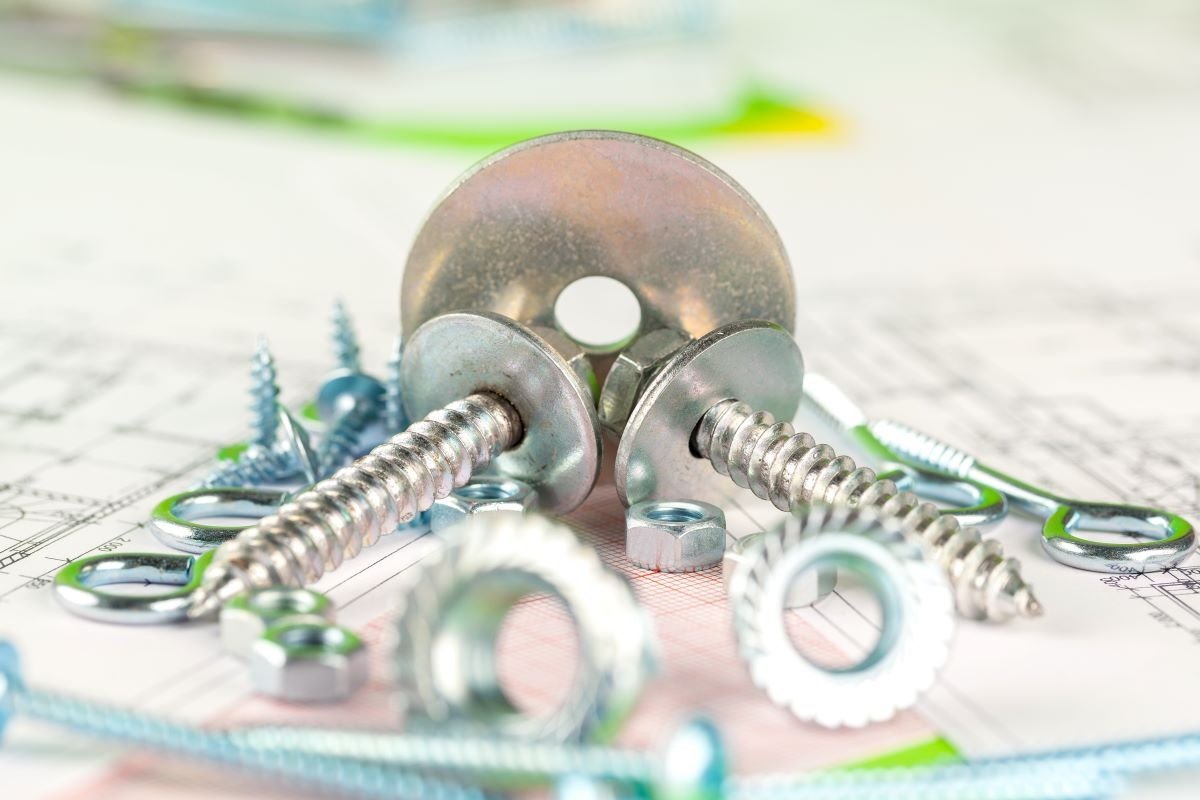
A washer is a thin, circular, metal disc with a hole in the middle, typically placed under the head of a bolt. Washers are used with bolts and nuts, where they are placed on the surface of the object being fastened. They help prevent damage to the connection points and are usually made from softer materials than the object being fastened. Common materials for washers include bronze, sheet metal, brass, lead, mild steel, copper, and aluminum.
Where Are Washers Used?
Washers serve the purpose of distributing the load of a nut or bolt head over a larger surface area. They are also used when the hole in the primary part is larger than the bolt’s diameter. In environments where vibrations are present, washers, nuts, or locking plates are used to prevent the loosening of bolts. Washers are used during the assembly of machine parts and threaded components like nuts and bolts to prevent surface damage and loosening of the connection.
Washer Manufacturing
Washers come in various types depending on their intended use. They can be flat, square, curved, spring, serrated, conical, or Allen types, among others. The dimensions of washers are determined by their nominal diameter, hole diameter, outer diameter, thickness, and weight. Washer manufacturing starts with cutting raw material sheets, followed by stamping in high-tonnage eccentric presses. The production process continues with inspection, sorting, vibration testing, polishing, and packaging. Washers can be produced in various types and materials according to the requirements.